
AI has become the defining technology of the decade, reshaping business, science, and the digital economy at unprecedented speed. Companies are integrating AI into workflows, governments are launching national AI programs, and global investment is rising in every sector.
Yet despite this explosive growth, new research shows a striking reality:
People around the world remain more concerned than excited about AI.
According to a major survey by the Pew Research Center covering 25 countries, a majority of adults express caution, uncertainty, or outright anxiety about AI’s growing role in daily life. Many respondents said they are:
- more fearful than optimistic,
- unsure whether AI benefits society,
- and worried about how fast the technology is advancing.
This tension rapid corporate adoption vs. slow public trust, is now one of the most important dynamics shaping the future of AI worldwide.
What the Global Survey Actually Shows
Pew’s cross-country survey highlights several clear trends:
1. High Awareness, Low Comfort
Most adults know about AI, but only a minority feel positively about its expansion.
2. Uneven Adoption Across Countries
In some nations, enthusiasm is growing (e.g., parts of Asia).
In others, skepticism dominates (e.g., Europe, Latin America).
3. Many People Prefer Cautious or Restricted AI Deployment
A sizable share of the global public wants tighter rules, more transparency, and slower rollout of high-impact AI systems.
4. Concerns Influence Political and Social Debate
As AI adoption accelerates, public unease is shaping conversations around:
- job security
- data protection
- fairness and discrimination
- misinformation
- safety of autonomous systems
This creates an atmosphere where AI’s economic momentum clashes with social hesitation.
Why Are People Worried? Four Core Fears Around AI
Even though AI promises major benefits, public concern is rooted in four areas:
1. Privacy & Surveillance
AI systems are often trained on:
- online behavior
- user data
- biometric information
- public posts
- workplace logs
Many fear that widespread AI adoption will erode personal privacy and enable mass surveillance, both by corporations and governments.
2. Job Displacement
The International Labour Organization (ILO) warns that AI poses real risks to:
- clerical roles
- routine administrative work
- customer support
- data processing jobs
- entry-level office positions
While AI can create new jobs, it can also automate old ones faster than societies can adapt.
3. Fairness & Bias
People worry about:
- biased algorithms
- unfair decisions
- discrimination in hiring or lending
- AI systems reinforcing stereotypes
Unequal outcomes have already been documented in multiple countries, fueling global mistrust.
4. Social & Ethical Risks
Concerns include:
- misinformation
- deepfakes
- loss of human connection
- erosion of creativity
- overdependence on technology
- safety of autonomous systems
Many feel AI is growing too fast, without enough guardrails.

The “Hype vs. Reality” Gap in AI Adoption
While everyday people remain cautious, businesses, industries, and governments are adopting AI at record speed. This creates an unusual global divide:
1. Corporations Are Racing Ahead
Companies see AI as a tool for:
- boosting productivity
- automating repetitive work
- reducing operational costs
- improving decision-making
- gaining competitive edge
This explains why firms adopt AI much faster than the public embraces it.
2. Workers Feel Uneasy
Employees often don’t get clear communication about:
- how AI will affect their roles
- what changes are coming
- what skills they’ll need in the future
This lack of transparency increases anxiety.
3. Governments Are Conflicted
Governments want the economic benefits of AI, but also need to protect citizens.
This leads to:
- national AI strategies
- safety regulations
- data protection laws
- policy debates
- public hearings
The world is still searching for the right balance.
Why Global Sentiment Matters
Public perception will shape the future of AI just as much as technology itself.
If people don’t trust AI:
- adoption may slow
- governments may impose stricter rules
- companies may face backlash
- misinformation fears may rise
On the other hand, if concerns are addressed, AI can become a transformative tool for:
- healthcare
- education
- climate science
- economic growth
- accessibility
- public services
Trust is the foundation, and right now, trust is uneven.
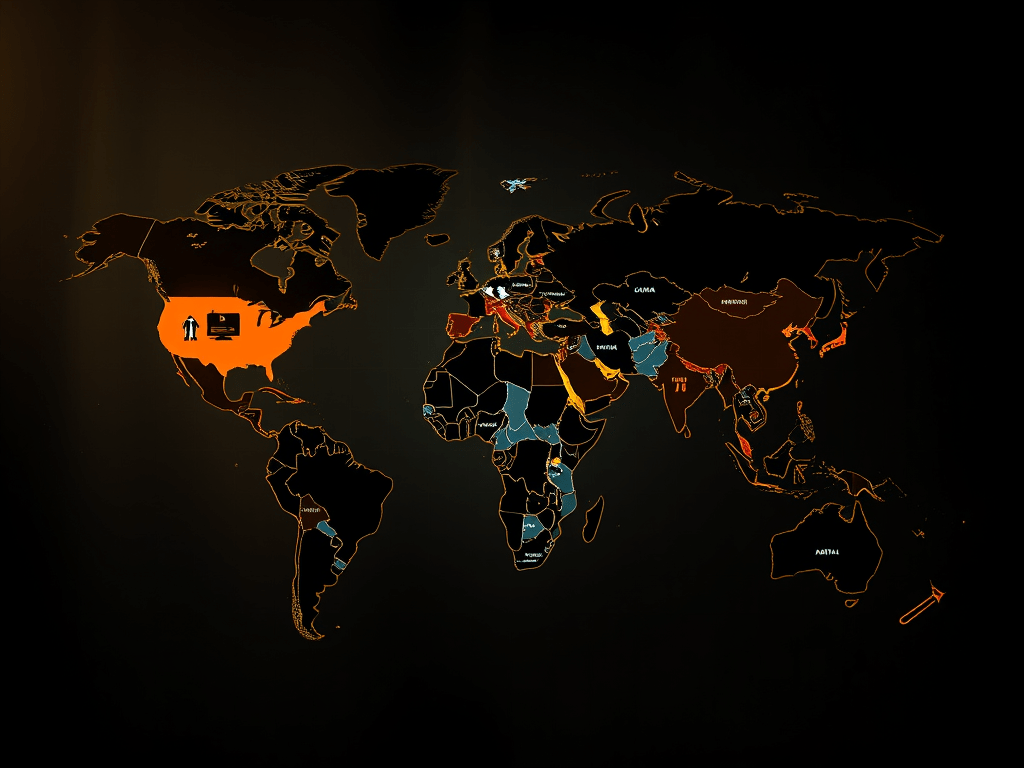
Five Regions, Five Different Views on AI
1. North America
Mixed sentiment, excitement in tech hubs, concern among workers about automation and misinformation.
2. Europe
One of the most skeptical regions due to strong privacy expectations and cultural emphasis on digital rights.
3. Asia
Higher optimism, especially in countries investing heavily in tech and automation (South Korea, Singapore, Japan).
4. Latin America
Greater fear of job loss, digital inequality, and surveillance.
5. Africa
Growing interest in AI for agriculture, education, and public services, but concerns about access and fairness persist.
This global variability means AI companies cannot adopt a one-size-fits-all approach.
The Path Forward: What Needs to Change
For AI adoption to reach its full global potential, three things must improve:
1. Clear, Transparent Communication
People want to know:
- how their data is used
- what AI systems can or cannot access
- whether jobs will be affected
- what safety features exist
Transparency builds trust.
2. Responsible Governance
Countries must strengthen:
- privacy protections
- model accountability
- safety testing requirements
- fairness standards
Public trust rises when regulation keeps pace with innovation.
3. Inclusive, Fair AI Development
AI should work for everyone, not only for wealthy countries, corporations, or elite industries.
Global policies need to reduce inequalities, not widen them.
Conclusion: The World Wants AI, But With Guardrails
The Pew Research Center survey reveals a powerful truth:
People aren’t rejecting AI, they just want it handled carefully.
The global public is aware of AI’s potential, but still uneasy about:
- rapid automation
- personal data risks
- fairness and bias
- job displacement
- social disruption
As AI becomes more embedded in life, companies and governments must ensure the technology grows responsibly, ethically, and inclusively.
The future of AI isn’t just about innovation.
It’s about earning human trust.


Leave a comment