
In the global race to dominate artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and next-generation data-center infrastructure, the world’s largest technology firms are making one major strategic shift: they are borrowing money at unprecedented levels.
Instead of relying solely on their massive cash reserves which historically served as a symbol of Big Tech’s financial strength companies like Amazon, Microsoft, Alphabet, Meta, and even Nvidia are increasingly turning to bond markets to raise capital.
According to analysts, this new approach marks a major turning point in how tech giants finance growth, and it may carry more risk than many investors realize.
The surge in debt issuance comes as AI investments skyrocket. Building AI supercomputers, expanding cloud capacity, and developing next-gen chips require tens of billions of dollars and the pace is accelerating. But the choice to borrow rather than spend cash signals a shift in corporate strategy that goes far beyond technology.
In this blog, we’ll explore why Big Tech is issuing debt, what it means for the broader market, and why some analysts are sounding the alarm.
Why Big Tech Companies Are Issuing More Debt Than Ever
Tech giants have long been admired for their enormous cash reserves, often holding tens or even hundreds of billions of dollars. But despite this liquidity, several are now tapping bond markets at a record pace. Why?
1. AI Has Triggered the Largest Capital Expenditure Boom in Tech History
Artificial intelligence isn’t cheap far from it.
Companies investing heavily in AI infrastructure are spending on:
- Massive data centers
- Power-hungry GPU clusters
- Custom silicon (chips)
- Networking and cooling systems
- AI research infrastructure
- Global expansion of cloud regions
Microsoft alone has hinted at $50 billion+ in annual AI-related capex, while Amazon and Alphabet are not far behind. Borrowing helps finance these massive expansions without draining cash balances.
2. Debt Is Cheaper Than Using Cash for Many Corporations
Even with higher interest rates compared to recent years, corporate borrowing remains relatively attractive for major tech firms because:
- Their credit ratings are extremely strong
- Market demand for corporate bonds remains high
- Interest paid on debt can be tax-deductible
- Holding cash provides strategic flexibility
From a balance-sheet perspective, issuing debt allows companies to preserve liquidity while still pursuing aggressive investments.
3. Bond Markets Offer an Almost Unlimited Pool of Capital
There is huge investor appetite for high-quality corporate debt especially from companies like Microsoft, Apple, Amazon, and Alphabet.
Institutional investors, pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, and insurance companies all view Big Tech bonds as safe havens.
This allows tech companies to raise tens of billions quickly and with minimal friction.
Why Analysts Are Becoming Concerned
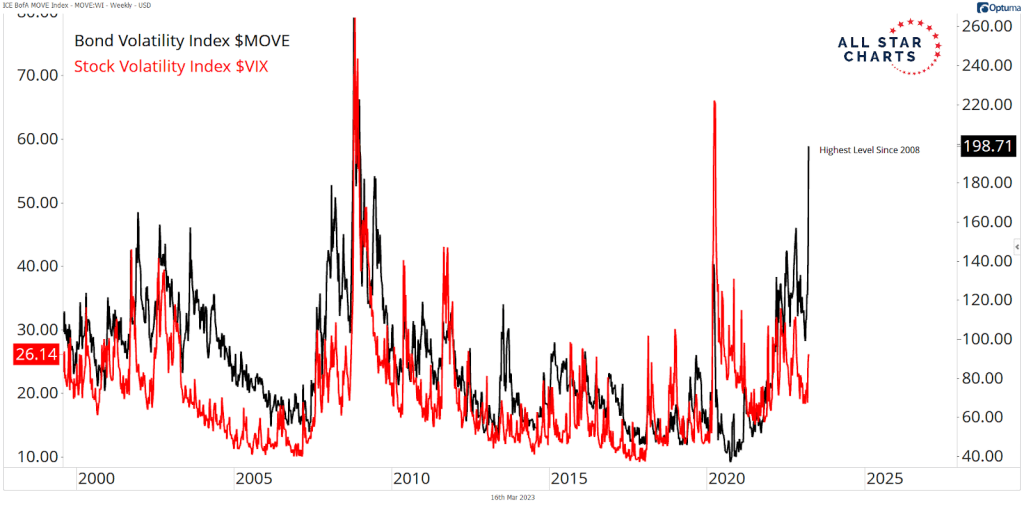
While issuing debt itself is not dangerous, analysts warn that the scale and speed of this borrowing spree could introduce new risks into both the tech sector and broader financial markets.
1. Higher Debt Levels Reduce Financial Flexibility
Big Tech companies have historically stood out for being:
- Low-debt
- High-cash
- Ultra-stable
This made them some of the safest companies in the world.
But the more debt they accumulate, the more their risk profile begins to resemble that of traditional capital-intensive industrie like telecom or energy.
More debt means:
- Higher interest payments
- Greater sensitivity to rate hikes
- Pressure on future cash flows
A decade ago, this would have been unthinkable for tech giants.
2. AI Investments Are Expensive and Returns Are Uncertain
AI is revolutionary, but monetizing it at scale has proven difficult.
Even major players admit that:
- AI models are expensive to train
- Cloud margins can shrink due to GPU costs
- Enterprise AI adoption is slower than expected
- Profit cycles lag far behind investment cycles
If AI revenues do not grow fast enough, tech companies could be left servicing massive debt loads with lower-than-expected returns.
3. Rising Corporate Leverage Could Create Market Fragility
Tech is the backbone of today’s stock market.
If tech companies become more sensitive to economic cycles due to high debt, that fragility will spill over into:
- Stock indexes like the S&P 500 and Nasdaq
- Corporate bond markets
- Pension funds and institutional portfolios
In other words, more debt = more systemic risk.
4. A Shift Away from Cash Resilience
Big Tech’s legendary cash piles acted as a stabilizer for markets.
When crises emerged from the dot-com crash to the 2008 recession to COVID-19, these companies emerged stronger because they didn’t depend on borrowing.
If cash reserves stop growing or shrink due to massive AI spending, that safety cushion erodes.
AI and Data Centers: The New Capital-Intensive Frontier
To understand why companies are taking on so much debt, it’s important to recognize how drastically the industry is changing.
AI and cloud infrastructure are becoming the new “digital factories”
Much like manufacturing companies build factories, modern tech companies must build:
- AI supercomputers
- Massive GPU clusters
- Renewable energy–powered data centers
- High-density server farms
- Global fiber networks
This shift makes tech more capital-intensive than ever before.
Nvidia GPUs are the new oil
Demand for GPUs has exploded:
- $20,000+ per unit
- Thousands needed for AI clusters
- Lead times stretching months
- Fast depreciation cycles
To keep up, companies must spend billions, quickly.
How Much Debt Are Tech Giants Taking On?
While exact numbers vary by quarter, recent trends show:
- Microsoft has issued tens of billions for cloud + AI
- Amazon raised billions to expand AWS data centers
- Alphabet is borrowing to expand global infrastructure
- Meta issued debt to support AI training and metaverse projects
- Nvidia is using debt to support supply chain and R&D scaling
This wave of borrowing is unprecedented in Big Tech history.
Is This Trend Sustainable?
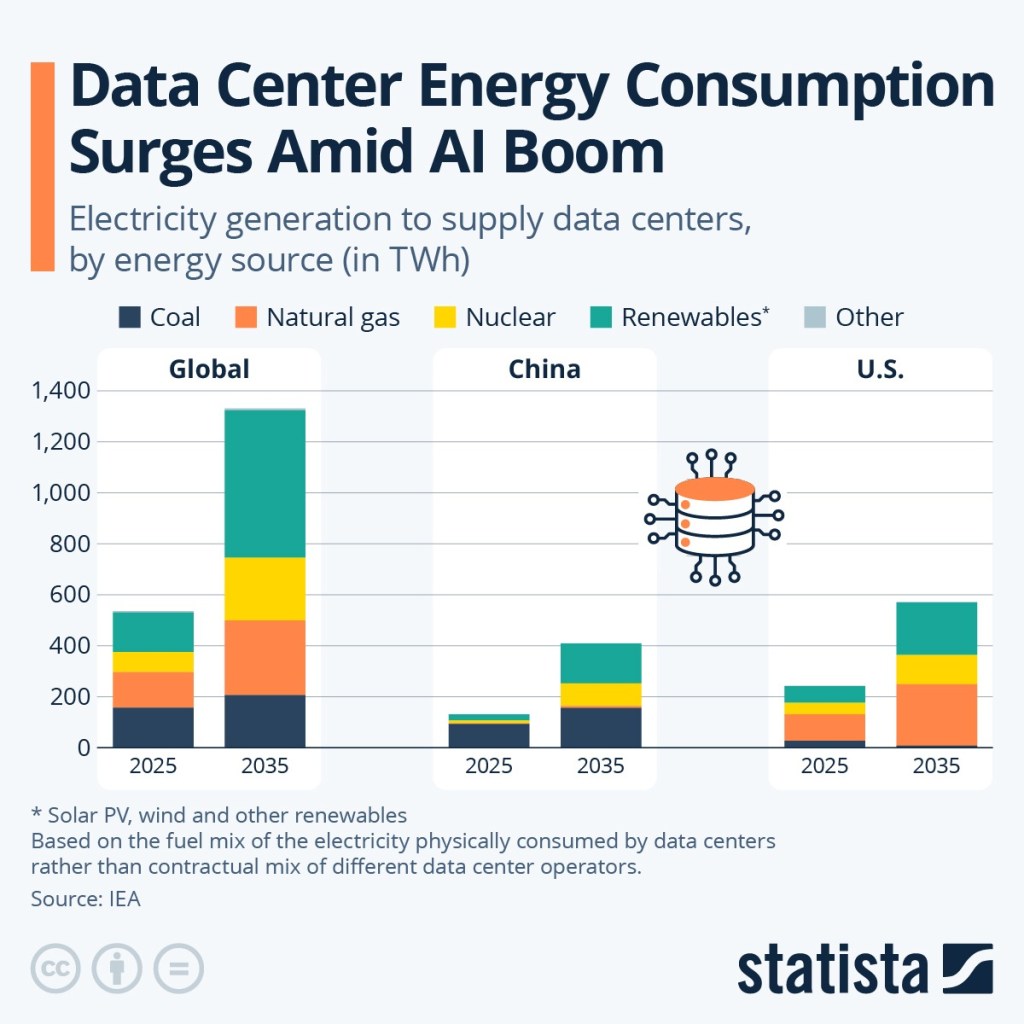
The answer depends on several future factors:
1. AI must become significantly more profitable
If AI revenues scale quickly, the debt will be worthwhile.
2. Interest rates must remain stable or decline
Higher rates would make refinancing more expensive.
3. Energy and infrastructure costs cannot spiral out of control
Data centers already consume massive amounts of electricity.
4. Competitors must avoid a “spending arms race”
If every tech giant overspends, many may struggle to break even.
Conclusion: A High-Stakes Bet That Could Reshape the Tech Sector
Big Tech’s shift toward debt-funded AI investment marks one of the most important financial transformations in the digital era.
While borrowing brings strategic advantages preserving cash, lowering tax burdens, and accelerating growth, it also introduces new vulnerabilities.
The tech sector is transitioning from “light, asset-efficient innovation” to “heavy, capital-intensive industrialization.”
This transition comes with:
- Higher financial risk
- Greater market sensitivity
- Larger systemic implications
Analysts aren’t predicting a crisis, but they are warning that the tech sector’s unprecedented borrowing spree should not be overlooked.
AI may be the future, but it is also incredibly expensive and Big Tech is betting billions that it will pay off.



Leave a comment